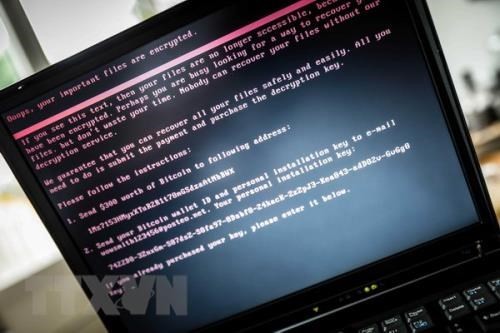
They comprised 968 deface, 635 malware and 1,556 phishing attacks.
According to the MIC’s Authority of Information Security, cyber security and safety in Vietnam has been improved over the past time thanks to campaigns on malware removal and training courses on cyber attack combat launched in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
However, the number of computers infected with malicious viruses (botnet) in the country in May and June exceeded 1.37 million, higher than 850,000 recorded in April.
A report released by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in late March 2019 shows that Vietnam was ranked 50th out of 175 places of 194 countries worldwide in the global cyber security index, up from the 100th position in 2017.
The country ranked 11th among 38 countries in Asia-Pacific, and fifth out of 11 countries in Southeast Asia in this regard, after Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand and Indonesia.
The ministry said malware–related attacks on Government computers doubled in during the period, and experts called for more attention to malware prevention and control on Government computers in the time ahead.
























