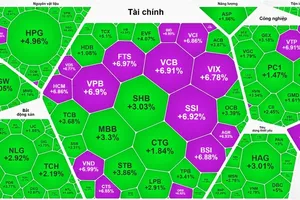
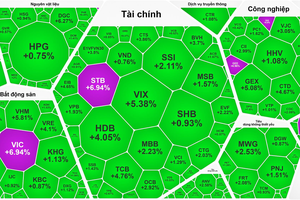
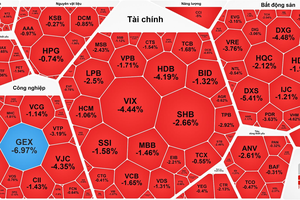
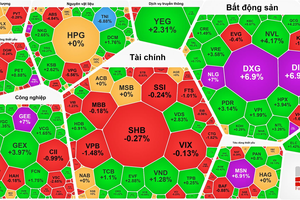
After the losing trading session on January 28, the most exciting topic on securities forums at that time was ‘What makes the stock market so volatile?’. Investors cited all the reasons, even conspiracy theories, such as market manipulation by the "strong hands" and cornering the market combined with shutting down the trading system. Not so many investors dare to accept the truth that they were the reason for those fluctuations.
When stocks climb up wildly, no one mentions their extraordinary excitement but immerses in the increasing profits day by day, feeling the joy of gaining a few more percentage points of profit every day. When the market flips over, the crowd unexpectedly becomes concerned about the management responsibilities of the regulator for such a sudden plummet in the market. They seem to think that the regulator must make the market go up.
From a psychological perspective, trying to find external reasons to explain an adverse outcome or a mistake of oneself is actually an avoidance of responsibility or a state of trying to soothe the pain. This kind of sentiment is quite common in the stock market. Therefore, books on securities investment and trading all emphasize the principle of eliminating emotions from decisions.
This principle has only a few short lines, but it is summarized in hundreds of years of securities trading of investors. Many new investors in the stock market only want to see drawings describing investment strategies and tips on making stock investments profitable, easy to understand and practice immediately. However, they are reluctant to absorb the experiences written in multi-page books.
They know the support, resistance, and technical buy point of stocks. However, they do not understand the risk-return tradeoff principle in each transaction, the win/loss ratio, and the principles of capital management, trading, portfolio building, and risk management.
F0 investors - newcomers to the market - before every decision to buy or sell, usually pay attention to profit first. Meanwhile, experienced investors often concern about the maximum risk they will encounter and whether it is worth the expected return or not. For instance, when an investor decides to buy stock A at VND25,000 per share, if he thinks that the price will go up to VND30,000 in the next week, giving him a profit of 20 percent, then he is an F0 investor.
On the contrary, if he thinks that the price of stock A does not increase as expected but decreases, so he will cut loss at VND24,000, then he is an Fn investor. When putting risks before profits, investors are responsible for their capital and have determined that securities investment is a long-term career instead of an opportunity to make money quickly.
The fierce turbulences, like the market volatility last week, have occurred many times in the past 10 years and contributed to eliminating several generations of amateur investors. What goes up must come down: that is the rule. Market trends also have many different levels.
A long-term uptrend based on macroeconomic growth or micro-growth of enterprises still mixes with short-term downtrends when supply and demand dominate in a period. The current market is a short-term downtrend in a long-term uptrend. Therefore, long-term investors do not need to panic, even though the downward volatility can reach dozens of percentage in just a few days. It is an opportunity to restructure the portfolio, take partial profits on the portfolio, and buy back stocks at lower prices, or even buy more stocks.
In contrast, short-term speculators have to focus on protecting cash assets. For not knowing whether we are making long-term investments or speculating, it will lead us to emotional transactions going along with the majority and being dominated by unusual movements in the market. Worse, we will trade stocks erratically, making consecutive mistakes and being kicked out of the game.
When stocks climb up wildly, no one mentions their extraordinary excitement but immerses in the increasing profits day by day, feeling the joy of gaining a few more percentage points of profit every day. When the market flips over, the crowd unexpectedly becomes concerned about the management responsibilities of the regulator for such a sudden plummet in the market. They seem to think that the regulator must make the market go up.
From a psychological perspective, trying to find external reasons to explain an adverse outcome or a mistake of oneself is actually an avoidance of responsibility or a state of trying to soothe the pain. This kind of sentiment is quite common in the stock market. Therefore, books on securities investment and trading all emphasize the principle of eliminating emotions from decisions.
This principle has only a few short lines, but it is summarized in hundreds of years of securities trading of investors. Many new investors in the stock market only want to see drawings describing investment strategies and tips on making stock investments profitable, easy to understand and practice immediately. However, they are reluctant to absorb the experiences written in multi-page books.
They know the support, resistance, and technical buy point of stocks. However, they do not understand the risk-return tradeoff principle in each transaction, the win/loss ratio, and the principles of capital management, trading, portfolio building, and risk management.
F0 investors - newcomers to the market - before every decision to buy or sell, usually pay attention to profit first. Meanwhile, experienced investors often concern about the maximum risk they will encounter and whether it is worth the expected return or not. For instance, when an investor decides to buy stock A at VND25,000 per share, if he thinks that the price will go up to VND30,000 in the next week, giving him a profit of 20 percent, then he is an F0 investor.
On the contrary, if he thinks that the price of stock A does not increase as expected but decreases, so he will cut loss at VND24,000, then he is an Fn investor. When putting risks before profits, investors are responsible for their capital and have determined that securities investment is a long-term career instead of an opportunity to make money quickly.
The fierce turbulences, like the market volatility last week, have occurred many times in the past 10 years and contributed to eliminating several generations of amateur investors. What goes up must come down: that is the rule. Market trends also have many different levels.
A long-term uptrend based on macroeconomic growth or micro-growth of enterprises still mixes with short-term downtrends when supply and demand dominate in a period. The current market is a short-term downtrend in a long-term uptrend. Therefore, long-term investors do not need to panic, even though the downward volatility can reach dozens of percentage in just a few days. It is an opportunity to restructure the portfolio, take partial profits on the portfolio, and buy back stocks at lower prices, or even buy more stocks.
In contrast, short-term speculators have to focus on protecting cash assets. For not knowing whether we are making long-term investments or speculating, it will lead us to emotional transactions going along with the majority and being dominated by unusual movements in the market. Worse, we will trade stocks erratically, making consecutive mistakes and being kicked out of the game.