By integrating digital tools and technologies, schools can modernize the learning process and improve student outcomes. A collaborative effort between teachers and schools is crucial to remove the hurdles preventing successful digital transformation in education to foster innovation and enhance the quality of education.
Recognizing the potential of social media, teacher Vo Thi Hieu Thao at Tan Dinh Kindergarten proactively established YouTube and Facebook pages for her class. This innovative approach allows her to share regular updates on children's activities, fostering better communication and reducing the need for time-consuming parent-teacher interactions.
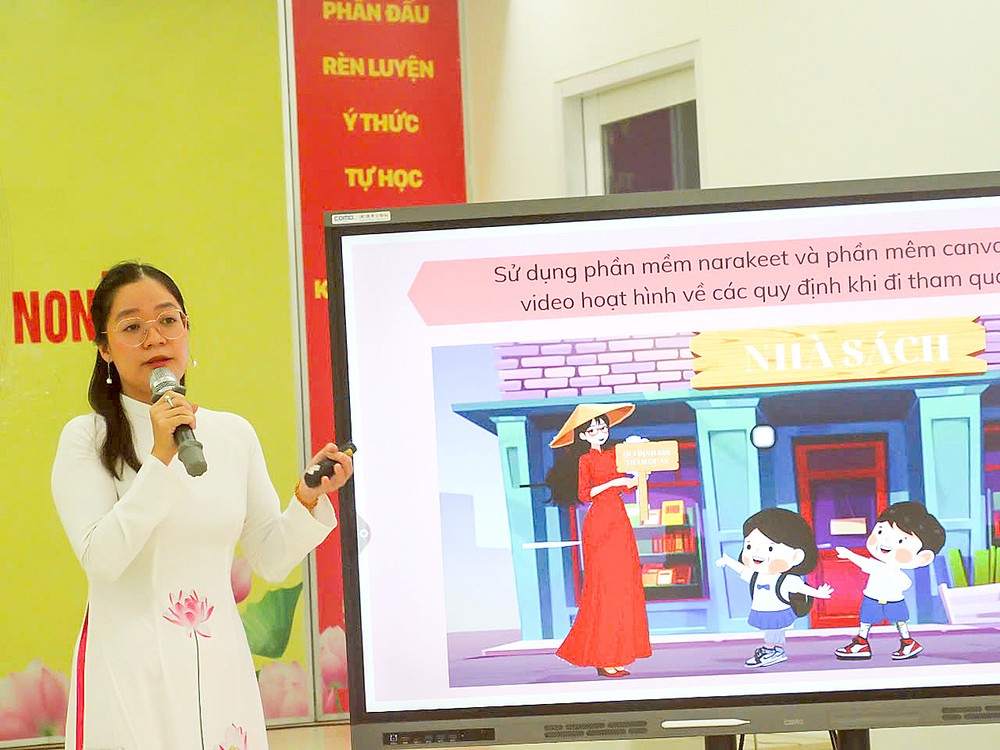
To further strengthen the school-family partnership, teacher Hieu Thao utilizes Google Forms to conduct online surveys, gathering valuable feedback from parents on their children's learning experiences. Recognizing the developmental stage of 4-5-year-olds who are unable to read, she thoughtfully incorporates engaging elements like animations and short films with voice-overs into her lesson presentations to captivate small learners.
Teacher Vo Thi Hieu Thao said that upon recognition that each student learns differently, prompting her to explore various teaching tools and continue using those that prove effective, while seeking alternatives for those that do not.
Teacher Nguyen Thi Ngoc Hanh at Trieu Thi Trinh Primary School admitted the importance of integrating information technology into her teaching practice. She views this as an ongoing learning process that allows for continuous exploration and adaptation.
She emphasized that the limited exposure to digital transformation during teacher training necessitates continuous professional development for educators. Furthermore, she highlighted the subject-specific nature of technology integration, noting that the effective application of information technology in teaching social sciences differs significantly from its application in natural sciences.
In District 11, a review of digital learning materials utilized during the 2023-2024 school year revealed a significant disparity in resource availability between natural sciences and social sciences. Mathematics emerged as the subject with the highest number of digital lessons, totaling 326.
A leader of the Department of Education and Training in District 11 emphasized the importance of a comprehensive digital resource bank, encompassing documents, textbooks, digital lectures, and multimedia resources. This centralized repository, they explained, would streamline lesson planning for teachers and contribute to a more consistent and equitable quality of education across all schools.
Head of the Department of Education and Training of District 10 Nguyen Thanh Trung commented that currently, there is no digital transformation model that is suitable for all schools, but each unit has different conditions in terms of facilities, qualifications and capacity of teachers. Therefore, each school needs to choose a suitable solution, maximizing the initiative and creativity of the management staff and teachers.
Meanwhile, Head of the Department of Education and Training of Tan Binh District Phan Van Quang said that digital transformation has many advantages when implemented for students at higher education levels, but at the two levels of preschool and primary education, it is still limited due to the specific number of teachers/class allocation as well as the ability of students to receive.
The Ministry of Education and Training is currently seeking public input on a draft circular outlining a Digital Competency Framework for learners within the national education system. This framework aims to establish a standardized set of digital skills and knowledge that students should acquire throughout their education.
The draft framework outlines six core digital competencies: data and information utilization, effective communication and collaboration in digital environments, digital content creation, safe digital practices, problem-solving using digital tools, and the application of artificial intelligence. This framework serves as a guiding reference for establishing standards and provides a foundation for educational institutions to design and implement curricula, learning materials, and teaching methodologies that effectively cultivate digital competencies among students.
In Ho Chi Minh City, beginning with the 2024-2025 academic year, the education of digital citizenship skills will be formally implemented in primary schools. This initiative will encompass four instructional methods including the teaching of Information Technology in accordance with the 2018 General Education Program, the integration of digital citizenship skills education into other subject areas, the enrichment of digital citizenship skills content through various activities and the establishment of clubs dedicated to digital citizenship skills education for students.
Deputy Director of the Ho Chi Minh City Department of Education and Training Nguyen Bao Quoc emphasized that enhancing digital skills among high school students is a crucial objective in achieving a holistic educational framework. This is particularly significant as the entire sector advances towards digital transformation.
The cultivation of digital competencies is expected to positively influence students' attitudes and behaviors in scientific research endeavors, thereby aiding in their future career paths.