Over the past years, healthcare facilities in Ho Chi Minh City have been actively applying information technology in management, operations, and patient services. Many digital transformation solutions have been implemented such as registration for medical examinations using chip-based citizen identification cards; cashless payments; appointment scheduling; and management of medical records using electronic codes
Suffering from diabetes and chronic hypertension for more than 5 years, a 58-year-old patient has to regularly visit Gia Dinh People’s Hospital every month to queue for a number to see the doctor and undergo laboratory tests. Previously, she had to leave early in the morning and return past noon, carrying various documents such as her health insurance card, citizen identification card and medical examination book.
Recently, however, her medical examination time has been significantly reduced, and she can receive her medication and leave by just after 10 AM. This is all thanks to the application of the chip-attached citizen identification card integrated with the health insurance card.
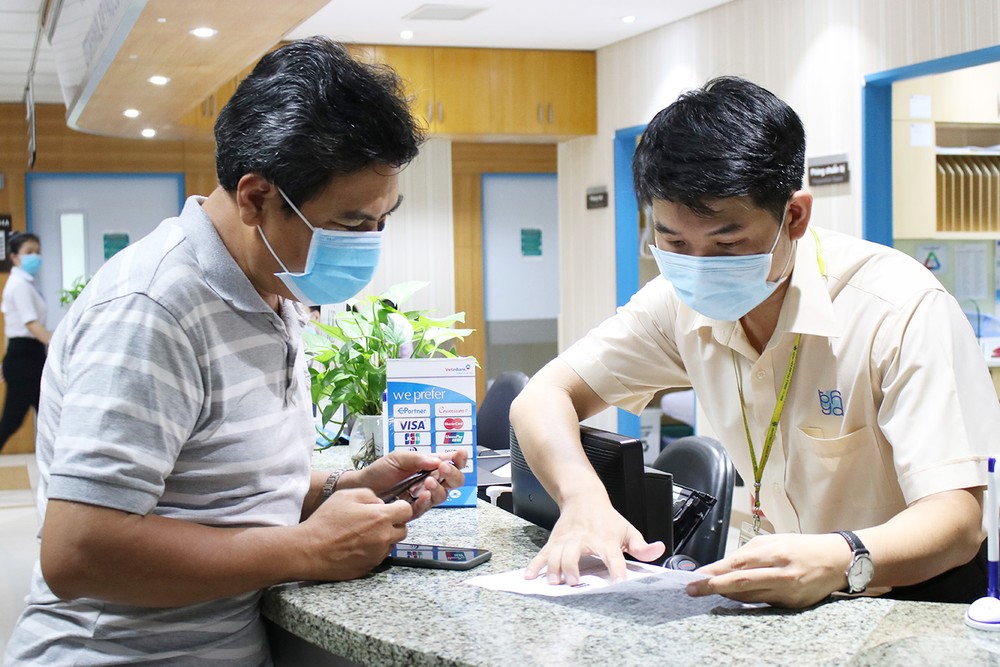
Meanwhile, at HCMC’s Phu Nhuan District Hospital, two smart kiosks have recently been introduced to help patients register for medical examinations, pay hospital fees using citizen identification cards, and use facial recognition, significantly reducing waiting times and making it convenient for patients.
Dr. Vo Van Minh, Director of Phu Nhuan District Hospital, stated that the hospital receives about 1,000 patients daily, not including those coming for regular health check-ups.
For the past few years, the hospital has implemented automatic number retrieval and cashless payments via QR code scanning, but these were isolated solutions. The new kiosk solution integrates multiple features at once, connecting chip-based citizen identification cards and biometrics. Therefore, patients only need to authenticate using facial recognition for subsequent visits.
According to Deputy Director Nguyen Truong Nam of the Information Technology Bureau under the Ministry of Health, hospital digitalization is the standardization of information, data, and the formation of a data warehouse to serve management, medical examination and treatment, and patient care (before, during, and after examination and treatment). The criteria for hospital digitalization need to focus on meeting three noes including no paperwork, no queuing, and no cash.
To date, all medical facilities have deployed a Hospital Information System, connected to 63 health insurance agencies in 63 provinces and cities, and deployed remote and online appointment booking.
In addition, nearly 100 hospitals have implemented electronic medical records, eliminating the use of paper medical records while health stations have deployed management software; plus, more than 61 percent of clinics and public health centers have deployed electronic prescribing and interlinked databases with the national information system on prescription management.
All medical examination and treatment facilities and medical human resource training facilities under the management of the Ministry of Health have cashless payment services in many forms such as bank transfer, QR code scanning, electronic wallets, and medical examination cards connected to banks.
The effectiveness of digitalization is clearly demonstrated for both hospitals, patients, and the health sector. For hospitals, digitalization has contributed to improving the quality and efficiency of hospital management; improving the quality of examination, treatment, and patient care; saving costs, and making hospital operations transparent; increasing competitiveness, attractiveness, and patient satisfaction. Patients can experience and use high-quality medical services.
For the health sector, hospital digitalization will form specialized data warehouses, data warehouses for medical examination and treatment, and data warehouses for electronic health records. These data warehouses are interconnected between medical facilities nationwide to support and improve the quality of providing healthcare and medical examination and treatment services for people.
From medical data warehouses, large data systems of the health sector will be formed, so that modern digital technologies such as big data, and artificial intelligence (AI) can be applied to serve scientific research, and analyze disease models, said Mr. Nguyen Truong Nam.