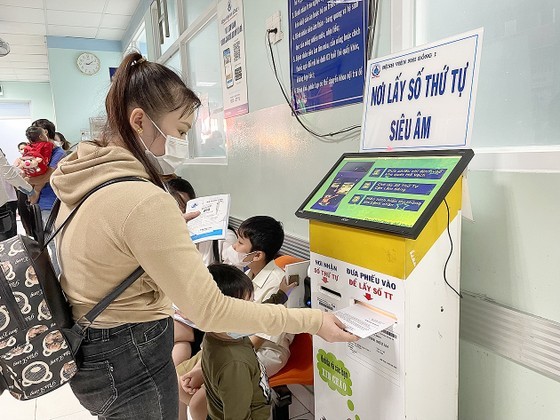
Parents are taking numbers to see doctors from electronic kiosks
Parents are taking numbers to see doctors from electronic kiosks
More than 10 years ago, HCMC -based Children's Hospital 1 started digitizing scans of health insurance documents, re-examination appointments, and patients’ certificates of leave for social insurance benefits.
Up to now, this unit has implemented many automated applications with an orientation toward smart health such as kiosks for taking numbers for automatic registration, kiosks for taking numbers for testing, and kiosks for looking up medical examination and treatment prices.
Thanks to the adoption of IT and technologies, patients cant register for online medical examinations via the website, phone, or mobile app; thus, they no longer have to wait in line.
Moreover, patients also do not use cash but pay via card, app, QR Code, or POS. In 2021, the hospital also deploys a payment solution via QR code that patients only need to scan the QR code in a doctor’s order to pay instead of taking the paper to the cashier.
HCMC-based Children's Hospital 1 is also one of the first hospitals in the country to build its own smart drug bidding software, digitizing all stages of the drug bidding process.
However, according to Dr. Ngo Ngoc Quang Minh, Deputy Director of Children's Hospital 1, the infirmary has bumped into a hiccup along the way for smart health. In particular, the most difficult problem is attracting and retaining IT human resources due to the low salary. Worse, many machines, equipment, and software are outdated and the equipment procurement was not done in time as it must wait for the city’s approval.
Hung Vuong Hospital is also one of the hospitals with a fast digital transformation speed, but according to hospital Director Associate Professor Hoang Thi Diem Tuyet, the hospital has faced many difficulties including slow mechanisms, processes and procedures while IT changes too fast rate.
Hung Vuong Hospital has implemented electronic medical records since 2020 and the hospital has so far finished all online outpatient medical records and inpatient obstetrical medical records. Sixty percent of gynecological inpatients and 40 percent of neonatal have online medical records. However, the most important issue of electronic medical records is the information security system and network security because if confidentiality is not ensured, it may lead to violations of the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment.
Financial issues are also a common challenge that hospitals have been facing in implementing digital transformation. Currently, the investment in information security systems costs more than VND10 billion, which is beyond the capacity of most hospitals.
Hospitals have sent their proposal for the purchase of a new IT system, but their proposals are not approved. While waiting for specific policies, in order to recruit and retain IT staff, hospitals need to save themselves by a solution that does not separate the IT team in the hospital from the medical examination and treatment team but integrates functions and tasks into joint activities directly or indirectly.
According to Dr. Nguyen Anh Dung, Deputy Head of the city Department of Health, from now to 2025 with a vision to 2030, the city's health sector has developed the project "Digital transformation and building smart healthcare" with the goal that all people will have electronic health records by 2025 and all hospitals manage patients by electronic medical records.
In addition, hospitals have deployed many IT applications to help detect and prevent epidemics in time, and manage non-communicable diseases in addition to building big data of the health sector including medical personnel, practice certificates, technical lists, and drug supply. The health sector in Ho Chi Minh City also deploys applications using big data to serve state management.